[ad_1]
Yves right here. Every now and then, there may be some excellent news on the environmental entrance. I ponder if the identical pattern towards decrease metropolis velocity is operative in Europe, or in the event that they had been already fairly tame resulting from larger bike prevalence and maybe additionally winding streets.
I additionally discover it humorous that the story is principally about Seattle however the photograph is clearly of New York Metropolis.
By Sarah Wesseler, a author and editor with greater than a decade of expertise protecting local weather change and the constructed surroundings. Initially printed at Yale Local weather Connection
 (Picture credit score: Anubhav Saxena on Unsplash)
(Picture credit score: Anubhav Saxena on Unsplash)
Since 2015, Seattle has lowered velocity limits throughout a lot of its highway community, setting residential streets at 20 miles per hour and most bigger city corridors at 25 miles per hour. After these adjustments took impact, research confirmed that automobile crashes fell by roughly 20%, whereas the crashes that did happen resulted in considerably fewer accidents.
Cities throughout the U.S. are following Seattle’s lead, with velocity limits dropping from Denver and Minneapolis to Washington, D.C., and Hoboken. Though these adjustments are motivated by the necessity to scale back deaths and accidents from automobile crashes, there’s a rising recognition that in addition they profit the local weather.
“Security and environmental targets go collectively. They’re inevitably interlinked,” stated Venu Nemani, the chief security officer of the Seattle Division of Transportation.
Excessive Pace Limits Are a Barrier to Local weather-Pleasant Transportation
Transportation is the biggest supply of emissions in the US, and passenger automobiles are the main offenders throughout the sector. Electrical automobiles can assist scale back these emissions, however they’re not a silver bullet — many consultants agree that assembly local weather targets may even require automobile use to fall. Consequently, it’s important for governments to assist individuals meet their wants by strolling, biking, and taking public transportation (which frequently requires touring on foot to a transit cease).
However reaching this may require making streets safer for individuals shifting round on foot or by bike, as issues over highway security are a typical barrier to strolling and biking. Sadly, these issues are justified. In response to the World Well being Group, greater than 1 million individuals die on roads yearly around the globe. Greater than half of all deaths and accidents from crashes contain weak teams akin to pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists.
In the US, pedestrian and bike owner fatalities have risen lately in opposition to the backdrop of a wider highway system failure that kills tens of hundreds of individuals yearly.
“Now we have a visitors dying disaster within the U.S.,” stated Alex Engel, senior supervisor of communications on the Nationwide Affiliation of Metropolis Transportation Officers. “Site visitors deaths are unbelievably excessive, particularly in comparison with our friends. They’re getting worse, for a wide range of totally different causes.”
Car velocity performs a significant position in these incidents, with quicker movement resulting in extra and deadlier crashes. Increased speeds are particularly harmful for individuals outdoors automobiles. In response to the AAA Basis for Site visitors Security, a pedestrian struck by a automobile touring at 23 miles per hour faces a ten% threat of dying. At 46 miles per hour, this rises to 90%.
A World Push for Safer Streets
The motion to decrease velocity limits in U.S. cities represents a much-needed break with the previous, Engel stated.
“The way in which we’ve set velocity limits within the U.S. for many years has been actually fairly outdated, and it was primarily based round basically pseudoscience,” he stated.
The normal technique basically permits drivers themselves to find out velocity limits. On this mannequin — nonetheless utilized in a lot of the nation — transportation officers measure the velocity at which all automobiles on a selected highway are shifting throughout a given interval with no visitors congestion, then decide the velocity above which the quickest 15% of this group are touring. This quantity (rounded) then turns into the brand new velocity restrict for the highway. Nevertheless, since some drivers journey above the posted restrict, this strategy causes velocity limits to rise over time.
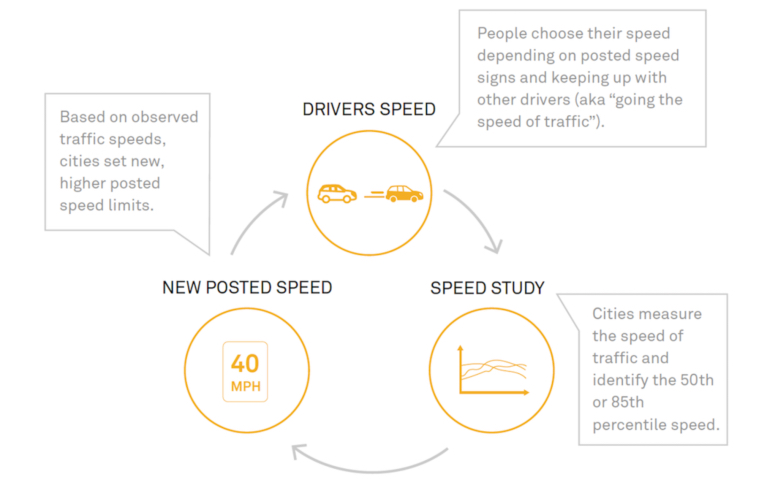
Efforts to maneuver past this strategy have been impressed by worldwide precedents. Imaginative and prescient Zero, a technique first adopted by Sweden’s parliament in 1997, has been significantly influential. Whereas conventional approaches to highway security emphasize people’ duty to forestall crashes, Imaginative and prescient Zero focuses on making a system during which human error — which is not possible to utterly get rid of — is much less prone to trigger critical hurt. Among the measures used to attain this embrace decreasing velocity limits, redesigning streets (by including roundabouts, for instance), and mapping crashes to allow stronger interventions in scorching spots.
One other power shaping the worldwide debate over visitors speeds is 20’s Lots for Us, a volunteer-driven group primarily based in the UK. The group was based in 2007 by Rod King, an avid bike owner who skilled the advantages of 20-mile-per-hour velocity limits whereas visiting the bike-friendly metropolis of Hilden, Germany. Variations of the marketing campaign’s title have been adopted as a slogan by transportation companies and advocates, with “20 is a lot” showing all over the place from buses in Washington, D.C. to yard indicators in Salt Lake Metropolis.
Policymakers throughout Europe and the U.S. have been receptive to Imaginative and prescient Zero and 20’s Lots concepts. In response to King, in the UK, 28 million individuals — practically 42% of the full inhabitants — now stay in a 20-mile-per-hour group. London has lowered its velocity limits, as have Brussels, Paris, and different European capitals. On the nationwide degree, Spain and Wales have set default limits of 30 kilometers per hour (round 19 miles per hour) and 20 miles per hour, respectively, on many roads.
Designing a Protected Transportation System
Wen Hu, a senior analysis transportation engineer on the Insurance coverage Institute for Freeway Security, has examined the results of decrease velocity limits in Seattle and Boston. She stated that these and comparable research from different nations have largely confirmed that decreasing velocity limits brings actual advantages. “Mainly, all this analysis tells the identical story: Lowering velocity limits can scale back rushing and scale back crash severity.”
Drawing on research from Hu and others, “Metropolis Limits,” a 2020 report printed by the Nationwide Affiliation of Metropolis Transportation Officers, concluded that the comparatively easy act of fixing velocity restrict indicators can result in a major return on funding for municipalities. “A rising physique of proof in locations like Seattle, Boston, and Toronto reveals that drivers reply to posted velocity limits even with none enforcement efforts,” the authors wrote.
However decrease velocity limits alone can’t utterly get rid of crashes, after all. Hu cautioned that whereas velocity restrict reductions are efficient, they should be mixed with different safety-focused interventions. “It’s not so simple as you simply scale back velocity limits and that solves the issue,” she stated.
The intervention most acquainted to many Individuals — police enforcement — is much lower than best, based on “Metropolis Limits.” The report’s authors write that police disproportionately cease individuals of shade when imposing visitors legal guidelines and that police-led velocity restrict enforcement can have damaging unintended penalties in communities of shade.
As an alternative, the report says, the simplest method to gradual visitors on streets the place rushing is widespread is to alter the bodily design and operation of the road itself; for instance, by including velocity humps and decreasing the size of inexperienced lights at cease indicators. Pace cameras can even assist.
Seattle Redesigns Its Streets to Defend Cyclists and Pedestrians
In recent times, Seattle has efficiently redesigned a lot of streets to gradual visitors, stated Clara Cantor, a group organizer with city advocacy group Seattle Neighborhood Greenways. Nevertheless, some streets nonetheless encourage rushing, and a excessive share of town’s 28 common annual visitors deaths happen on these corridors.
“There’s nonetheless some streets in Seattle which are actually designed like highways and really feel like you ought to be driving on it like a freeway. And that’s the place we’re seeing a lot of the main crashes the place individuals are dying,” she stated.
And although decrease velocity limits alone aren’t sufficient to forestall all deaths or change each driver’s conduct in a single day, they play an important position in “the lengthy recreation,” as Cantor put it. “Now, when SDOT (the Seattle Division of Transportation) goes in on each single a kind of streets, any little tiny mission that they’re doing, they’re designing for a decrease velocity restrict than they’d have been in any other case. And so over time that’s made a extremely large affect on loads of streets.”
Seattle Neighborhood Greenways remains to be pushing town to do extra to guard cyclists, pedestrians, and transit riders, however Cantor stated that even for cynical transportation activists, the division of transportation’s progress since adopting Imaginative and prescient Zero is spectacular. The expertise of biking across the metropolis “is totally, utterly reworked from the way it was in 2016,” she stated. “It’s manner, manner, manner, manner, manner higher and feels safer.” The general public transportation system has additionally grow to be extra sturdy, she famous, and pedestrian entry has improved.
These adjustments have made it simpler for individuals in Seattle to get round with out automobiles. “During the last decade, our inhabitants grew by about 20%, and through the identical time our visitors volumes just about stayed the identical on our [street] community, and our transit person ridership has grown by about 30%,” stated Venu Nemani. “We’re principally offering an increasing number of choices on daily basis for individuals of town of Seattle to make their journeys through the use of non-auto modes.”
In response to Rod King of 20’s Lots for Us, setting the stage for wide-ranging adjustments like these is a typical good thing about 20-mile-per-hour velocity limits. This makes velocity restrict reductions a important first step for cities wanting to enhance highway security and scale back emissions.
“The velocity of automobiles impacts your [road] crossings. It impacts what it’s a must to do to guard cyclists. It impacts what it’s a must to do to guard different motorists,” King stated. “So get the velocity down — get the kinetic power in a highway community down — and you can find you could have extra choices.”

[ad_2]
Source link



